To sign up for our daily email newsletter, CLICK HERE
In today’s data-driven world, there is a growing need to interpret and analyze vast amounts of data in a way that is easy to understand and interpret.
This is where heatmaps come in. Heatmaps are a powerful tool that can provide a visual representation of data that is both easy to understand and highly informative.
In this article, we will explore the concept of heatmaps, how they work, and some of their practical applications.
What is a Heatmap?
A heatmap is a graphical representation of data that uses color-coded cells to show different values. Heatmaps are often used to visualize large datasets and can help to highlight patterns and trends that might otherwise be difficult to spot.
Heatmaps can be created using a wide range of software, including spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel, and dedicated data visualization tools like Tableau and Python’s matplotlib library.
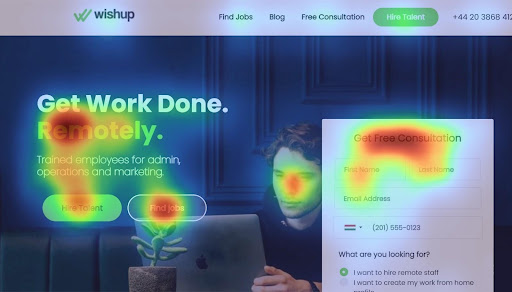
How do Heatmaps Work?
Heatmaps use color to represent different values in a dataset. Typically, a color gradient is used to represent the range of values in the dataset, with warmer colors (like red and orange) representing higher values, and cooler colors (like blue and green) representing lower values. Each cell in the heatmap represents a single value in the dataset, and the color of the cell corresponds to the value of that data point.
Practical applications of heatmaps
Heatmaps are a powerful tool that can be used in a wide range of applications. Some common applications of heatmaps include:
Website analytics
Heatmaps can be used to analyze website traffic and user behavior. For example, a heatmap might be used to show where users are clicking on a webpage, which can help to identify areas that need improvement.
Stock market analysis
Heatmaps can be used to analyze stock market data and can help to identify trends and patterns that might not be immediately apparent. For example, a heatmap might be used to show the performance of different stocks over a given time period.
Medical imaging
Heatmaps can be used in medical imaging to visualize areas of the body that are experiencing abnormal heat or inflammation. This can help doctors to identify and diagnose conditions like cancer and arthritis.
Environmental monitoring
Heatmaps can be used to monitor and visualize environmental data, such as temperature and air quality. This can help to identify areas that are experiencing unusually high levels of pollution or other environmental hazards.
Types of heatmaps
Heatmaps are a powerful tool for analyzing website user behavior. There are several types of heatmaps that can be used to gain insights into how users are interacting with a website. In this article, we’ll explore the most common types of heatmaps and how they can be used to improve website design and user experience.
1. Click Heatmaps
Click heatmaps are the most common type of heatmap. They show where users are clicking on a webpage by using colors to represent the frequency and intensity of clicks.
Click heatmaps can help you identify which areas of your webpage are the most popular with users and which areas are being ignored. This information can be used to optimize the placement of calls-to-action (CTAs) and other important elements on your webpage.

2. Scroll Heatmaps
Scroll heatmaps show how far down the page users are scrolling. They use colors to represent the percentage of users who reach each section of the page.
Scroll heatmaps can help you identify which parts of your webpage are getting the most attention and which parts are being overlooked. This information can be used to optimize the length and layout of your webpage.
3. Move Heatmaps
Move heatmaps show where users are moving their mouse cursor on a webpage. They use colors to represent the frequency and intensity of mouse movement.
Move heatmaps can help you identify which areas of your webpage are getting the most attention and which areas are being overlooked. This information can be used to optimize the placement of important elements on your webpage.
4. Attention Heatmaps
Attention heatmaps combine clicking, scrolling, and moving data to show where users are looking on a webpage. They use colors to represent the areas of the page that are receiving the most attention.
Attention heatmaps can help you identify which areas of your webpage are the most engaging and which areas are not. This information can be used to optimize the design and content of your webpage.
5. Form Analysis Heatmaps
The way people interact with the forms on your website is displayed by form analysis heatmaps. Fields that are being filled out and those that are being skipped are shown by different colors.
You can determine which fields are frustrating users the most and which regions are being abandoned by utilizing form analysis heatmaps. You may use this information to improve the layout and phrasing of your forms.
In conclusion, heatmaps are an effective tool for examining how users interact with websites. Move, scroll, pay attention, and analyze forms as you do so. With the use of heatmaps, you may determine which parts of your website are the most interesting, which parts are being neglected, and which parts require optimization.
Your website’s design and user experience may be enhanced by employing heatmaps, which may result in higher levels of user interaction, conversions, and income.
Why is it worth it to use if you are a UX designer
A crucial component of web design is user experience (UX) design. UX designers work to develop websites that are user-friendly, interesting, and cater to their demands.
Website heatmaps are one resource that UX designers may find very helpful. We’ll look at how website heatmaps may aid UX designers in refining their work and producing better user experiences in this post.
1. Identify user behavior
UX designers may learn how consumers interact with a website by using heatmaps. Heatmaps display which parts of the website are being visited the most and which parts are being neglected.
The positioning of calls to action, Exit Navigation, and other important aspects on the website may all be optimized using this data.
2. Optimize design elements
Heatmaps can help UX designers optimize the design of a website. By analyzing heatmaps, designers can identify which design elements are working well and which are not.
For example, heatmaps can help identify whether the color, size, or placement of a button is effective. This information can be used to make design changes that improve the overall user experience.
3. Improve content
UX designers may better understand how consumers interact with website content by using heatmaps.
Heatmaps may display which parts of a website are read and which are not. The quality and relevancy of the material may be improved with the use of this data, which might increase user happiness and engagement.
4. Test designs
Heatmaps can be used to test different design variations.
By creating heatmaps of different designs, UX designers can compare the effectiveness of different design elements. This can help designers make data-driven decisions about which design elements to keep and which to change.
5. Understand user preferences
UX designers may better understand user preferences by using heatmaps. Designers may determine which fonts, colors, and layout options are most successful in capturing users’ attention by analyzing heatmaps.
Designs that better suit the requirements and tastes of the consumers may be made using this knowledge.
Website heatmaps are a useful tool for UX designers, to sum up. Heatmaps may assist UX designers in producing better user experiences by studying user behavior, optimizing design components, enhancing content, testing designs, and understanding user preferences.
UX designers may build websites that are interesting, simple to use, and satisfy the demands of their consumers by adding heatmaps into their design process.
Conclusion
Heatmaps are a powerful tool that can provide a visual representation of data that is both easy to understand and highly informative.
Whether you are analyzing website traffic, stock market data, medical imaging, or environmental monitoring, heatmaps can help to highlight patterns and trends that might otherwise be difficult to spot. With the help of heatmaps, we can gain deeper insights into complex datasets and make more informed decisions based on the data we have.