To sign up for our daily email newsletter, CLICK HERE
A technical breakthrough in PCB design is the VIPPO PCB. An increasingly important use for vias in modern circuits is to enhance signal integrity and space efficiency.
This article will discuss and make a comparison between VIPPO and traditional HDI PCB.
HDI PCBs: The Evolution of Circuit Density
From Traditional PCBs to HDI PCBs
Electronic consumer goods have long employed conventional PCBs. The creation of HDI PCBs is a result of scientific advancements as well as consumer desire for smaller, more potent devices.
Vias and general lines in HDI PCB are different as compared to traditional PCB . HDI PCBs have made the number of connection pads on the board denser, thus placing more components on a smaller board.
HDI PCB: Function and Uses
Micro vias, buried, blind, and interconnected layers are part of HDI PCB. These features provide the potential to place more functionality in less space.
HDI PCBs are used in smartphones, tablets, and wearables. Automotive, medical, and aerospace use HDI PCBs for their devices.
Benefits of Using HDI PCB Technology
The great advantage of HDI PCBs is that they can contain much higher levels of complex and better-performing circuitry in reduced dimensions. This enables signals to move quickly and reduces signal loss, which has directly impacted overall device performance.
Increasing the density of PCBs will generally result in larger compactness in dimensions and, thereby, reduced weight. HDI PCBs are important for making miniaturized electronic products speedy and efficient.
VIPPO Technology: A Game Changer in PCB Design
In-depth Explanation of VIPPO Technology
VIPPO (Via-in-Pad Plated Over) is a huge breakthrough in PCB design. In this technology, the vias inside the component pads are formatted, which allows for plating over them.
In this way, the via and pad are considered as one, and the total area that a via and a pad would have taken separately has been saved. It makes the layout designs more compact and efficient, with improved signal integrity and better thermal management.
Distinguishing VIPPO from Traditional via Technologies
Traditional vias, such as through-hole vias and blind/buried vias, occupy much space in the PCB area and compromise signal integrity, especially when signal paths are long. VIPPO technology yields signal paths that are much shorter and more direct, hence improving electrical performance.
VIPPO PCB technology results in much mechanical stability and reliability because it precludes the possibility of pad cratering and delamination, which are common in traditional vias.
Application of VIPPO in Advanced Electronic Devices
The VIPPO technology is increasingly used in advanced electronic applications, where space, performance, and reliability are important. These include high-frequency RF and microwave circuits, and high-speed digital applications. VIPPO PCB is also used in compact consumer products that feature smartphones, tablets, and wearable electronics.
The added advantage of applying VIPPO will be in the automotive and aerospace industries, where solid PCB performance is desired. In its capability to enable enhanced performance and space use, VIPPO technology is altering the phase of modern electronic design.
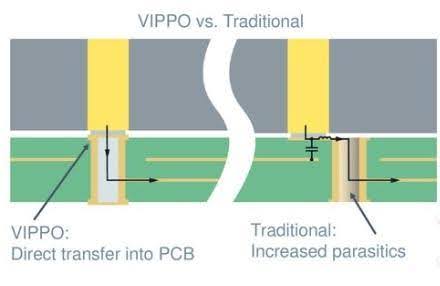
Head-to-Head: VIPPO vs Traditional HDI PCBs
Contrasting Design Methodologies
There is an absolute difference in the via integration way between VIPPO and traditional HDI PCB. Traditional HDI PCBs adopt such structures as micro vias, blind vias, and buried vias. They are usually positioned outside the component pads, which can lead to an unnecessary increase in area and may additionally increase the signal’s path. All this affects signal integrity.
On the other hand, VIPPO (Via-in-Pad Plated Over) technology integrates vias into component pads, saving a lot of space. Such a board design provides for small signal traces, which will minimize signal losses and, at the same time, boost signal integrity.
Through VIPPO, the use of space is optimized. Therefore, it finds applications very well in high-density or high-function applications.
Differences in Manufacturing Processes and Techniques
Another field in which the VIPPO PCB manufacturing process differs from that of conventional HDI PCBs is vias. Traditional HDI PCBs require plenty of drilling, plating, layering, etc., to make the vias that enable the interconnections between one layer of the board and another. The processes are fairly old, the manufacturing complexity is not high, and this positively affects cost.
VIPPO PCB technology requires more advanced techniques. The process includes drilling within the pads and careful plating. These are the two key parameters in the process that provide reliable interconnection. This added complexity makes the fabrication complex and increases costs since it requires specialized equipment and expertise.
With better performance and space efficiency resulting from this, the increase in production cost can be paid back, especially in high-end applications.
Comparative Performance and Reliability Analysis
VIPPO PCBs assure a better quality of the signals because the signal paths are shortened and directly connected. This reduces the loss of signals and allows the system to have the minimum level of interference. Hence ensuring good electrical performance under a very high frequency and high-speed application.
Moreover, the VIPPO technology promises better mechanical stability. Having these vias embedded inside the pads dramatically reduces the chance of cratering and delamination of pads, which are a high-case scenario for traditional vias.
An increase in reliability is very important, particularly for those applications in which reliability over time must be ensured, such as aerospace, automotive, and critical consumer electronics.
Although cheaper and easier to manufacture than VIPPO PCBs, traditional HDI PCBs are not as good in performance and reliability. Yet, they are a valid option in a wide variety of applications for which major concerns about cost are in order, extreme levels of signal integrity are not required, and space savings are not required.
VIPPO vs Traditional HDI PCBs: Key Technical Differences
| Feature |
VIPPO PCBs |
Traditional HDI PCBs |
| Via Configuration |
Vias integrated within pads |
Vias placed outside pads |
| Signal Quality |
Enhanced signal integrity |
Standard signal integrity |
| Fabrication Complexity |
Higher complexity |
Lower complexity |
| Cost Implications |
Relatively higher costs |
Cost-effective |
| Space Efficiency |
Greater use of space |
Moderate use of space |
The choice between VIPPO and traditional HDI PCBs is simply a function of application requirements such as performance, reliability, cost, and design constraints.
The Edge of VIPPO: Advantages Over Traditional HDI
Superior Electrical Performance with VIPPO
The electrical performance of VIPPO technology is great. Vias are integrated directly under the pads to minimize the length of signal paths. This leads to an increase in signal integrity and an important reduction in the respective signal losses. This important feature lends itself well to applications in high-frequency and high-speed conditions where the signal quality must be preserved.
Improved Thermal Management
One major advantage of VIPPO technology is its improved thermal characteristics. Enhanced heat dissipation has been crafted into the integrated via design. This ensures that electronic components are maintained and allows them to operate in optimum temperature ranges. Better thermal management is also key to the performance and life of the electronic device, especially in high-power applications.
Space Optimization for Complex Designs
Space utilization is a critical parameter with modern electronics, increasing the demand for small and powerful gadgets. VIPPO technology has the unique ability to utilize space in a manner unbeatable when greater numbers of components are packed in a narrow space. With increased optimization for space for the vias and pads put in separate layers to save more, the VIPPO mode is preferable for a compact and complex design of PCBs.
More Durable and Reliable
VIPPO PCB forms the basis of any reliability and durability in an electronic device. Putting vias within the pads of components reduces the risks of pad cratering and delamination, which are common with traditional vias.
This added mechanical stability ensures VIPPO PCBs can survive harsh operating conditions, and guarantee continued reliability, making them ideal for critical aerospace, automotive, and high-end consumer electronics applications.
Comparative Benefits of VIPPO and Traditional HDI PCBs
| Benefit |
VIPPO PCBs |
Traditional HDI PCBs |
| Electrical Performance |
Superior |
Good |
| Thermal Management |
Excellent |
Adequate |
| Space Utilization |
Optimal |
Standard |
| Reliability |
High |
Moderate |
These features make VIPPO a preferred option in advanced electronic applications where performance and reliability are critical.
Navigating the Challenges: VIPPO Implementation
Financial Considerations of Adopting VIPPO Technology
HDI technology is much more advanced in terms of processes and materials. VIPPO technology has a considerably increased cost over traditional HDI PCBs.
Technical Complexity and Manufacturing Challenges
High-precision drilling and plating within pads, necessary for implementing VIPPO, would add an additional level of complexity and potentially cause a production delay.
Need for Specialized Skills and Equipment
VIPPO-manufactured PCBs require highly skilled technicians and specialized equipment, which demands more investments in training and upgrading machinery.
Conclusion
While most areas of performance, reliability, and space considerations are better in VIPPO PCBs than in traditional HDI PCBs. VIPPO PCBs are more expensive and complex; specific needs for an intended application and budget provision determine the trade-off between VIPPO and traditional HDI PCBs.
Because PCB technology is likely to progress further, miniaturization and performance enhancement levels will reach newer levels that will propel innovation into the design of electronic devices.